Emotional intelligence harvard business – In the competitive world of Harvard Business, emotional intelligence (EI) has emerged as a cornerstone for unlocking individual and organizational success. Join us as we delve into the fascinating realm of EI, exploring its profound impact on workplace dynamics, leadership, decision-making, and innovation.
Emotional intelligence is a crucial skill for business leaders. By understanding their own emotions and the emotions of others, they can make better decisions and build stronger relationships. Business intelligence reporting tools can help leaders track their progress in developing emotional intelligence by providing data on their communication style, decision-making, and conflict resolution skills.
This data can be used to identify areas for improvement and develop strategies for enhancing emotional intelligence.
EI, the ability to understand, manage, and leverage emotions, has become an essential skill for thriving in the fast-paced and demanding environment of Harvard Business.
Emotional Intelligence in the Workplace

Emotional intelligence (EI) is the ability to understand and manage one’s own emotions and the emotions of others. It plays a vital role in the workplace, where individuals interact with each other and navigate complex situations on a daily basis.
To succeed in today’s competitive business environment, emotional intelligence is a crucial skill. Harvard Business School has recognized its importance and offers courses on the topic.
For those interested in developing their business intelligence capabilities, a business intelligence developer job description provides a comprehensive overview of the role and responsibilities involved in this field.
By honing both emotional intelligence and business intelligence skills, individuals can enhance their decision-making, leadership, and communication abilities, ultimately driving business success.
EI enhances workplace relationships by fostering empathy, communication, and conflict resolution. It improves productivity by reducing stress, increasing motivation, and enhancing decision-making. Organizations with employees who possess high EI experience increased profitability, customer satisfaction, and employee engagement.
Benefits of EI for Individuals
- Improved self-awareness and self-management
- Enhanced communication and interpersonal skills
- Increased resilience and stress management
- Greater empathy and compassion
- Improved decision-making and problem-solving
Benefits of EI for Organizations
- Increased productivity and efficiency
- Enhanced teamwork and collaboration
- Improved customer service and satisfaction
- Reduced absenteeism and turnover
- Increased profitability and organizational success
Measuring and Assessing Emotional Intelligence
Measuring and assessing EI is crucial for understanding an individual’s strengths and areas for development. Various methods exist, including:
Self-Report Measures
- Trait-based measures: Assess general EI characteristics
- Ability-based measures: Evaluate specific EI skills
Observer-Based Measures
- Behavioral interviews: Observe and assess EI behaviors
- 360-degree feedback: Collect feedback from multiple sources
Strengths and Limitations of Assessment Tools

Each assessment method has its strengths and limitations. Self-report measures provide subjective insights but may be influenced by self-bias. Observer-based measures offer objective data but require skilled observers. The choice of assessment method depends on the purpose and context.
Harnessing emotional intelligence is crucial for effective leadership and workplace success, as emphasized by Harvard Business. To enhance your understanding of business intelligence, consider exploring case studies here.
By integrating emotional intelligence with business intelligence, you can make data-driven decisions that resonate with both your team and customers, ultimately driving business growth and success.
Developing Emotional Intelligence: Emotional Intelligence Harvard Business
Developing EI is an ongoing process that involves:
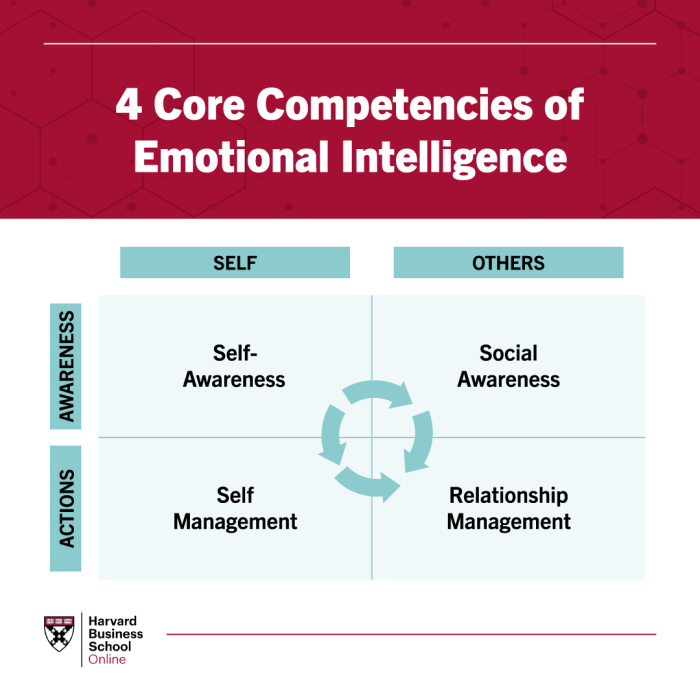
Self-Awareness
- Identify and understand one’s own emotions
- Recognize the impact of emotions on behavior
Self-Regulation
- Manage and control emotions effectively
- Adapt to changing situations and respond appropriately
Empathy
- Understand and share the emotions of others
- Develop compassion and understanding
Social Skills, Emotional intelligence harvard business
- Build and maintain positive relationships
- Communicate effectively and resolve conflicts
Effective Strategies for Developing EI
- Self-reflection and journaling
- Emotional intelligence training and workshops
- Coaching and mentoring
- Practice and application in real-world situations
Emotional Intelligence and Leadership
EI is essential for effective leadership. Successful leaders possess:
Emotional Self-Awareness
- Understand their own strengths, weaknesses, and emotions
- Manage their emotions under pressure
Emotional Regulation
- Control their emotions and avoid impulsive decisions
- Adapt to changing situations and lead with composure
Empathy
- Understand and connect with the emotions of followers
- Inspire and motivate through emotional connection
Social Skills, Emotional intelligence harvard business
- Build strong relationships with followers
- Communicate effectively and resolve conflicts
Impact of EI on Leadership Performance

- Increased team cohesion and productivity
- Enhanced decision-making and problem-solving
- Improved employee engagement and satisfaction
- Greater organizational success and profitability
Emotional Intelligence and Decision-Making
Emotions play a significant role in decision-making. EI helps individuals:
Understand Emotional Biases
- Identify and mitigate emotional biases, such as confirmation bias
- Make more rational and objective decisions
Consider Multiple Perspectives
- Empathize with different stakeholders and understand their perspectives
- Make decisions that balance emotional and logical considerations
Manage Stress and Pressure
- Control emotions under stress and make sound decisions
- Avoid impulsive or reactive choices
Impact of EI on Decision-Making
- Improved decision quality and effectiveness
- Reduced decision-making errors
- Increased stakeholder satisfaction
- Greater organizational success
Emotional Intelligence and Innovation
EI fosters innovation in the workplace by:
Encouraging Creativity
- Creating a safe and supportive environment for risk-taking
- Encouraging employees to express new ideas
Promoting Collaboration
- Building strong relationships and fostering teamwork
- Encouraging diverse perspectives and open communication
Managing Uncertainty
- Adapting to changing situations and embracing uncertainty
- Learning from mistakes and setbacks
Impact of EI on Innovation
- Increased creativity and new ideas
- Improved collaboration and knowledge sharing
- Enhanced risk-taking and experimentation
- Greater organizational innovation and success
Final Wrap-Up
As we conclude our exploration of emotional intelligence in Harvard Business, it becomes evident that EI is not merely a buzzword but a transformative force that empowers individuals and organizations to achieve extraordinary results.
By fostering self-awareness, empathy, and emotional regulation, EI unlocks a world of possibilities, driving innovation, enhancing leadership, and ultimately shaping the trajectory of success in the competitive landscape of Harvard Business.
FAQ Corner
What is the significance of emotional intelligence in Harvard Business?
EI is crucial in Harvard Business as it enables individuals to navigate complex social dynamics, build strong relationships, and make informed decisions in high-pressure environments.
How can I develop my emotional intelligence?
Developing EI involves self-reflection, practicing empathy, seeking feedback, and engaging in activities that enhance emotional awareness and regulation.
What are the key benefits of emotional intelligence for leaders in Harvard Business?
EI empowers leaders to inspire and motivate their teams, build trust, manage conflict effectively, and create a positive and productive work environment.